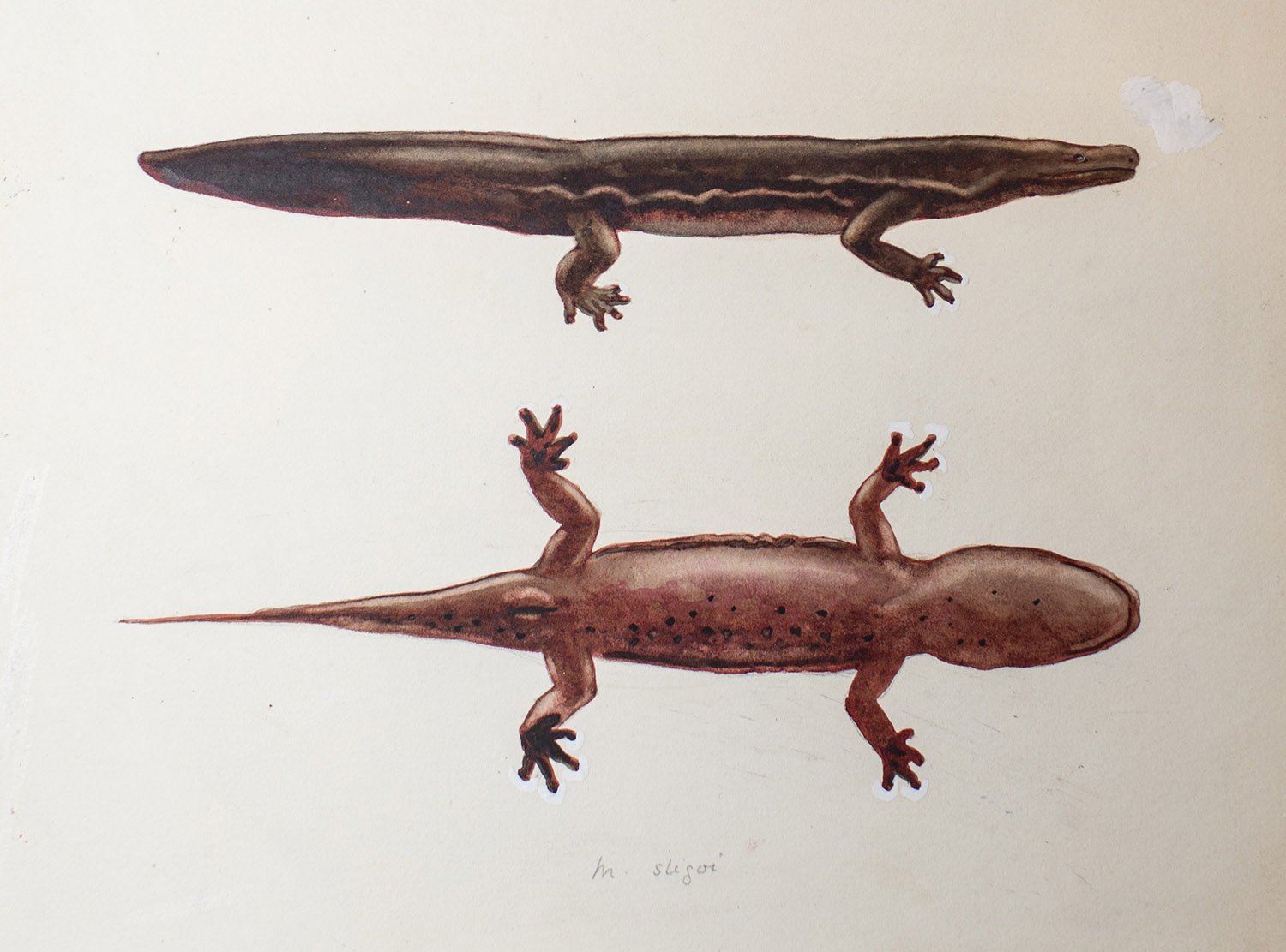
New species of giant salamander is world’s biggest amphibian
Using DNA from museum specimens collected in the early 20th century, researchers from ZSL (Zoological Society of London) and London’s Natural History Museum identified two new species of giant salamander – one of which they suspect is the world’s biggest amphibian. Chinese giant salamanders, now classified as Critically Endangered, were once widespread throughout central, southern … Read more