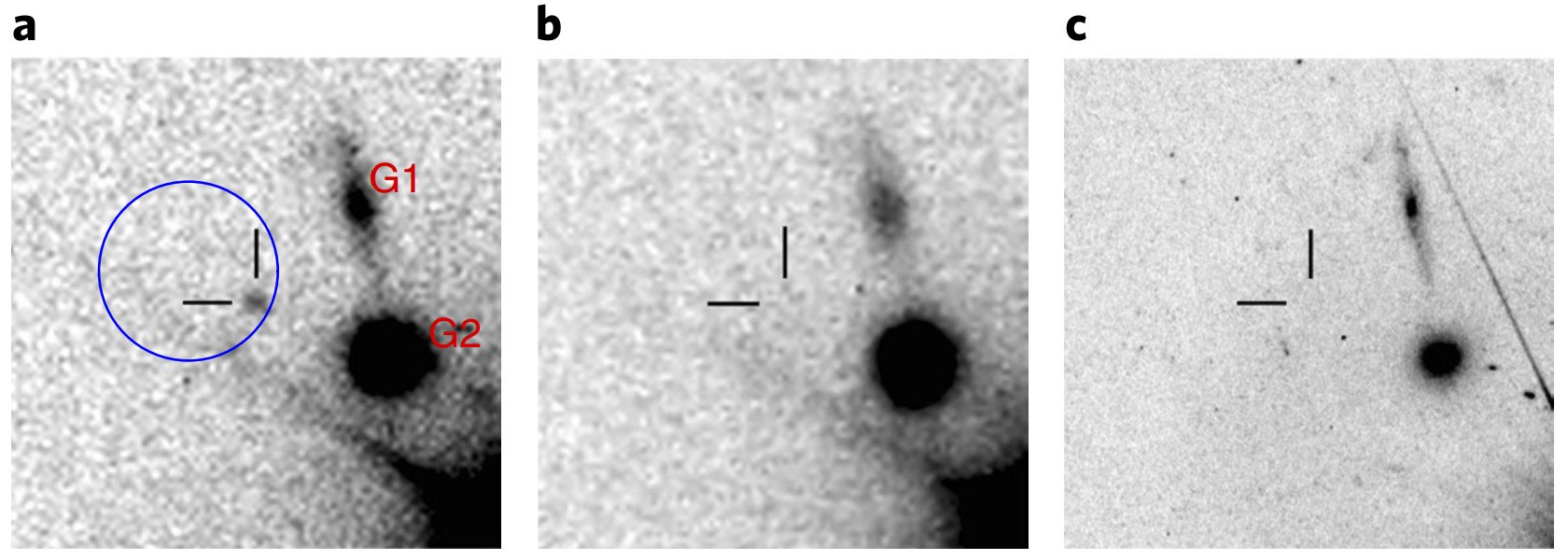
The “GRB case 070809” has been reopened: the “culprit” is a kilonova
An international team of astronomers identified a kilonova – or a very powerful cosmic explosion – associated with a gamma-ray burst recorded in 2007. The discovery was possible thanks to a careful study of archive data of the Keck and Hubble Space Telescope optical data and with the X-ray telescope, on board the satellite Neil … Read more