Studies of fungi provide new knowledge of harmful mutations in cells
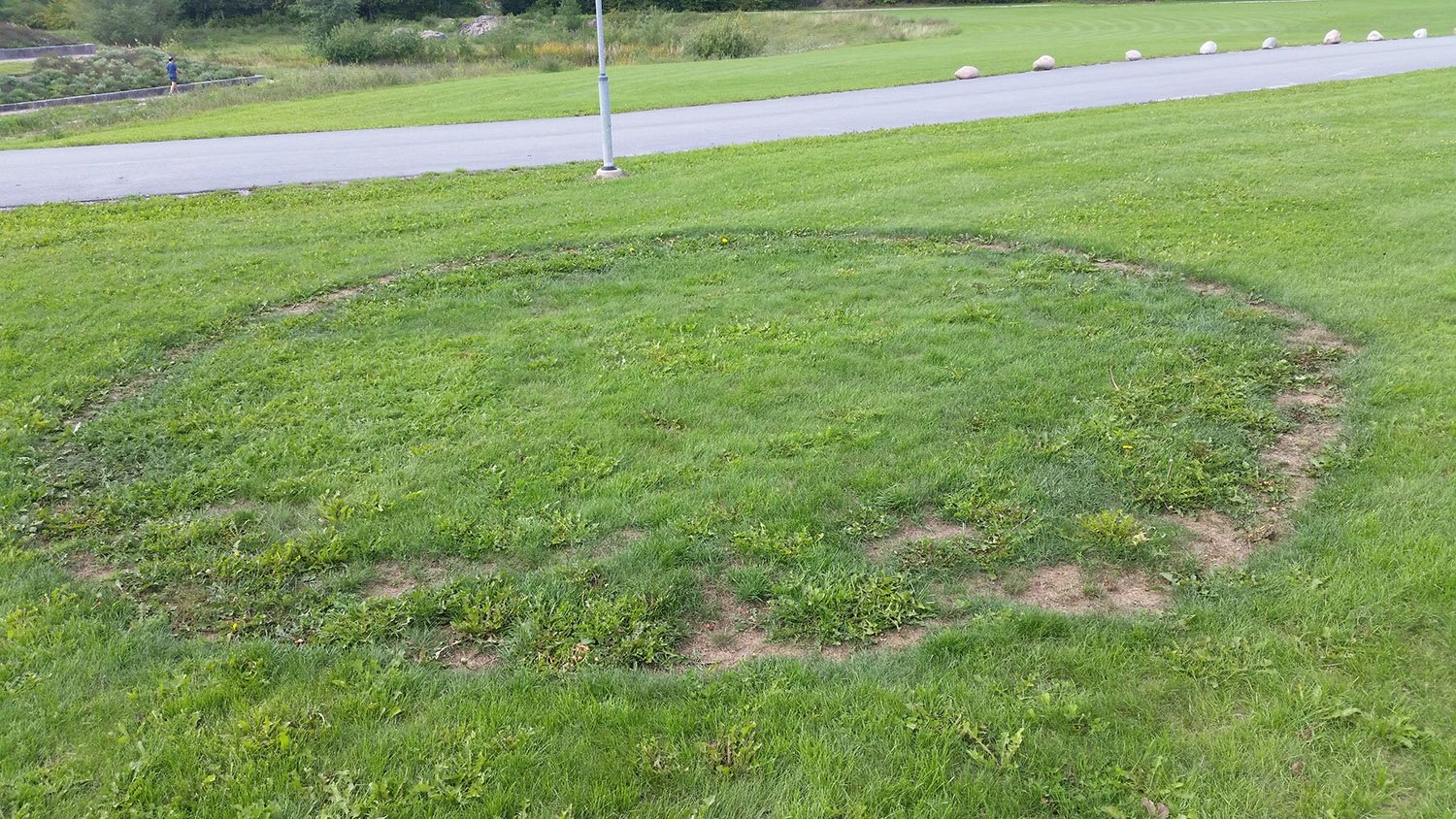
Long-lived mushrooms that grow in ‘fairy rings’ accumulate surprisingly few mutations over time. This finding indicates that their protection against harmful mutations is well developed. The results, to be published in the esteemed journal Current Biology, are interesting in terms of both medicine and evolutionary biology. In all living creatures, every cell contains DNA, which encodes … Read more