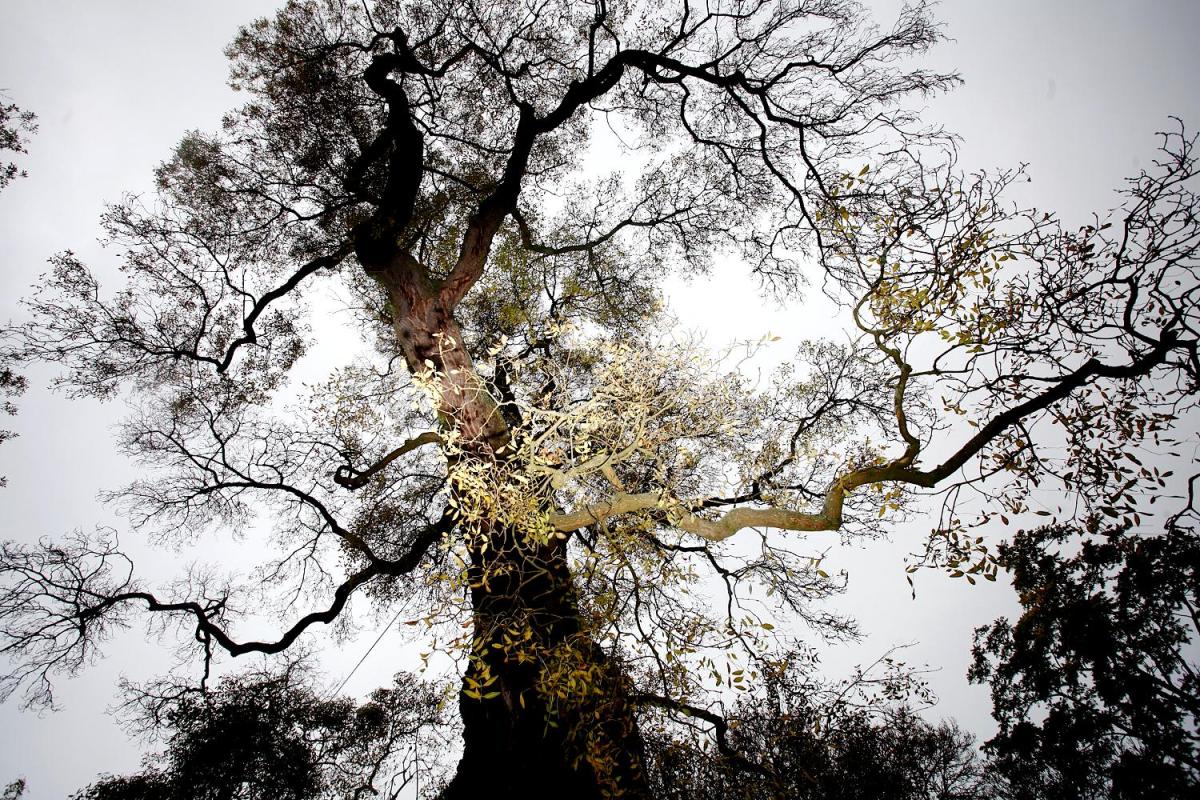
Scientists uncover resistance genes for deadly ash tree disease
New research has identified the genetic basis of resistance to ash dieback in UK trees, opening up new avenues for conservation. Researchers from Queen Mary University of London and the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew sequenced the DNA from over 1,250 ash trees to find inherited genes associated with ash dieback resistance. The study, published in … Read more