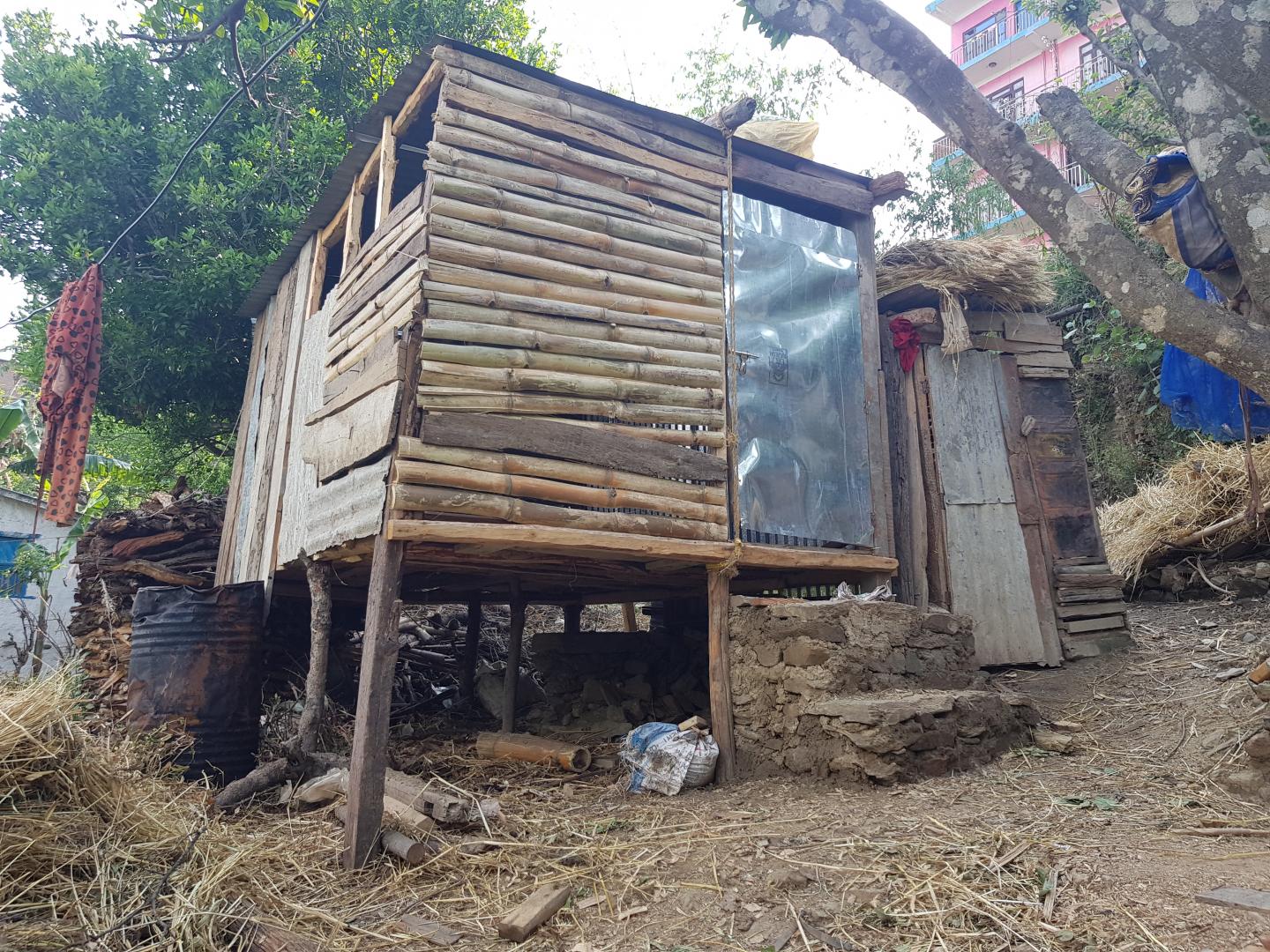
Women in Nepal still forced to sleep outside in ‘menstruation huts’
Despite being criminalised in 2018, an estimated 77% of girls in mid-Western Nepal are still being forced to sleep outside in “menstruation huts” during their period, according to a new study published today in Sexual and Reproductive Health Matters. All around the world, girls and women suffer from the stigma of menstruation. Nowhere is this more … Read more