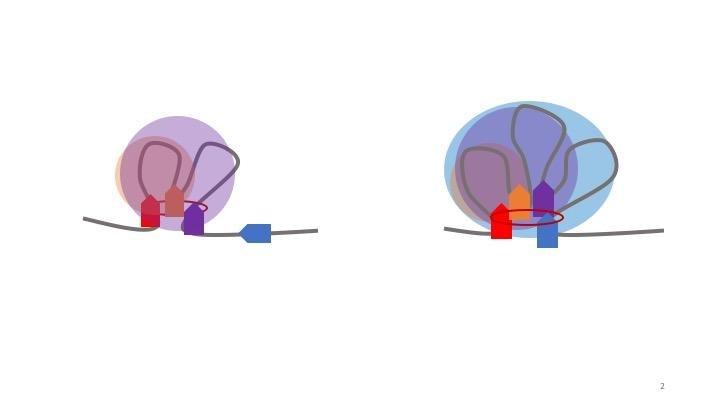
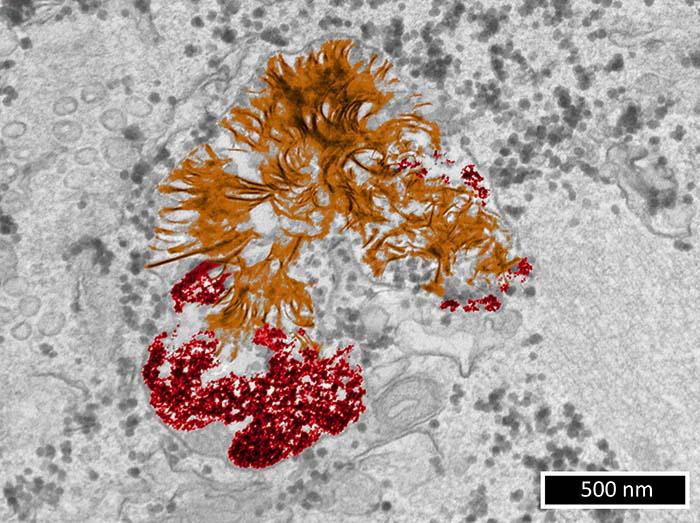
Artificial intelligence identifies previously unknown features associated with cancer recurrence
Artificial intelligence (AI) technology developed by the RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligence Project (AIP) in Japan has successfully found features in pathology images from human cancer patients, without annotation, that could be understood by human doctors. Further, the AI identified features relevant to cancer prognosis that were not previously noted by pathologists, leading to a … Read more