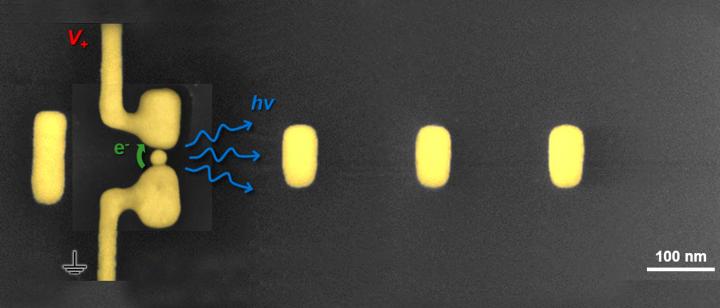
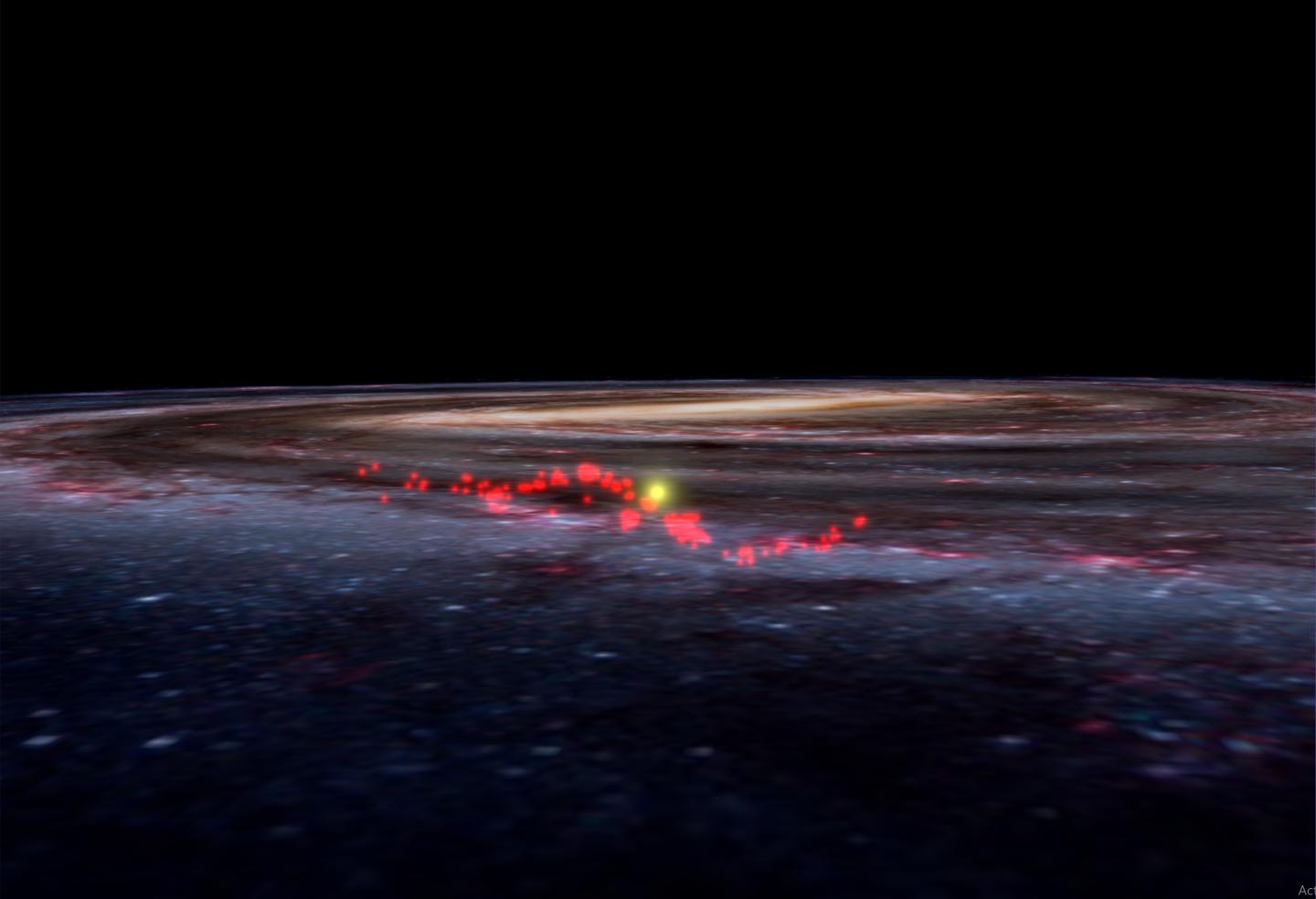
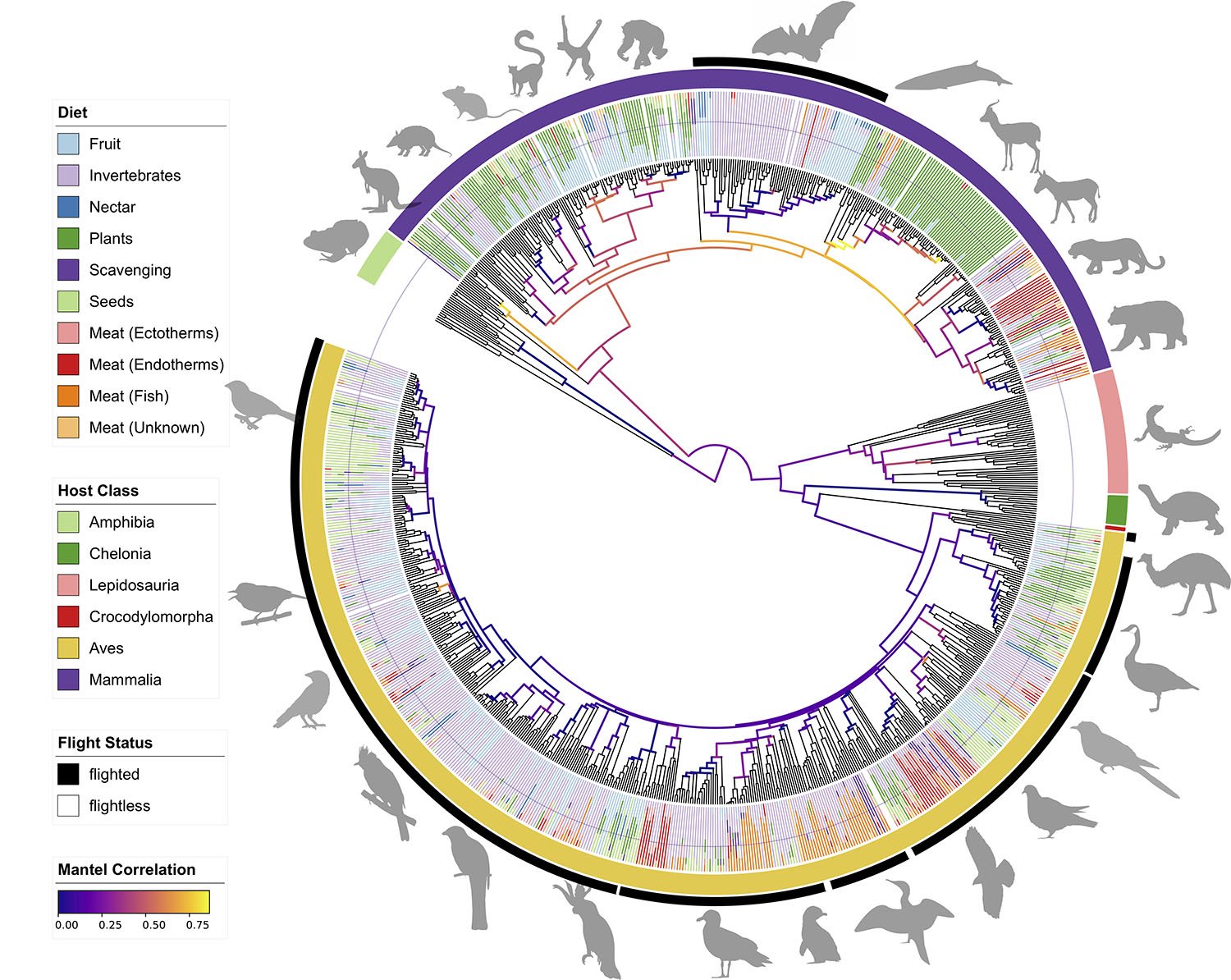
Sea-ice-free Arctic makes permafrost vulnerable to thawing
Permafrost is ground that remains frozen throughout the year; it covers nearly a quarter of Northern Hemisphere land. The frozen state of permafrost enables it to store large amounts of carbon; about twice as much as in the atmosphere. The rate and extent of future thawing of permafrost, and consequent release of its carbon, is … Read more