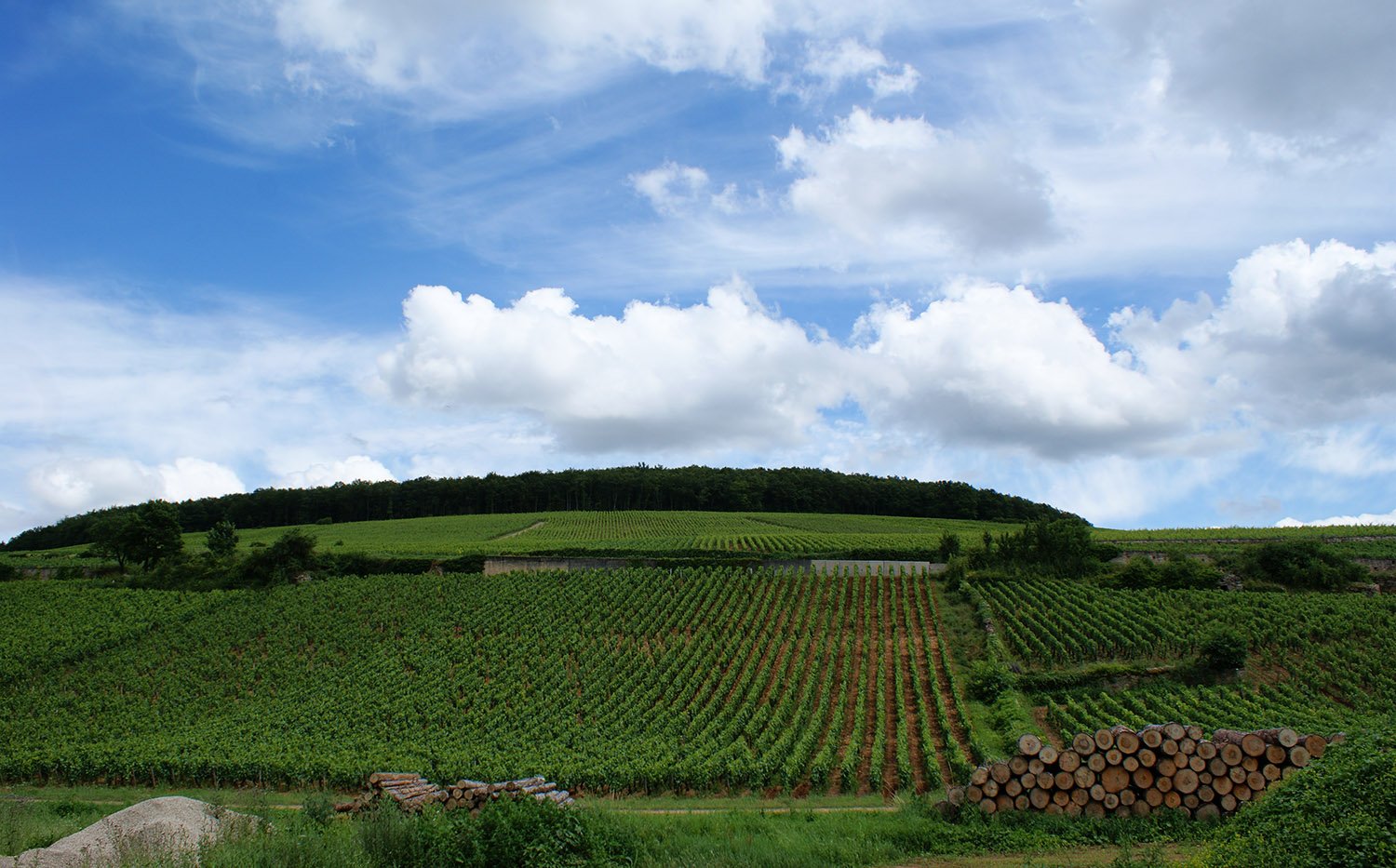
Burgundy wine grapes tell climate story, show warming accelerated in past 30 years
A newly published series of dates of grape harvest covering the past 664 years is the latest line of evidence confirming how unusual the climate of the past 30 years has been. The record shows wine grapes in Burgundy, eastern France, have been picked 13 days earlier on average since 1988 than they were in … Read more