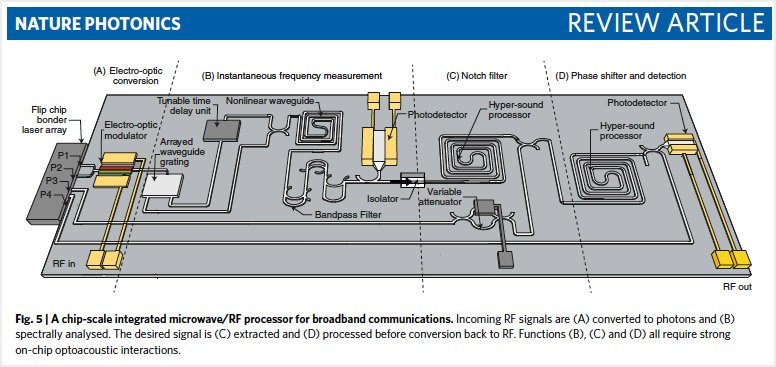
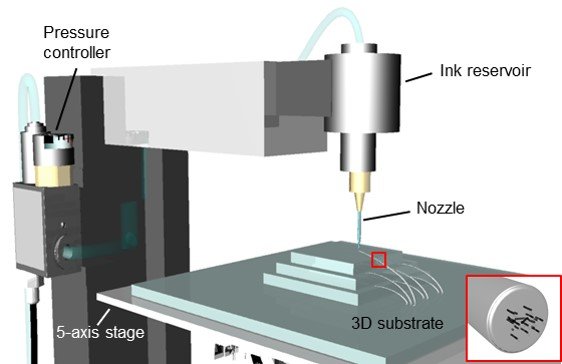
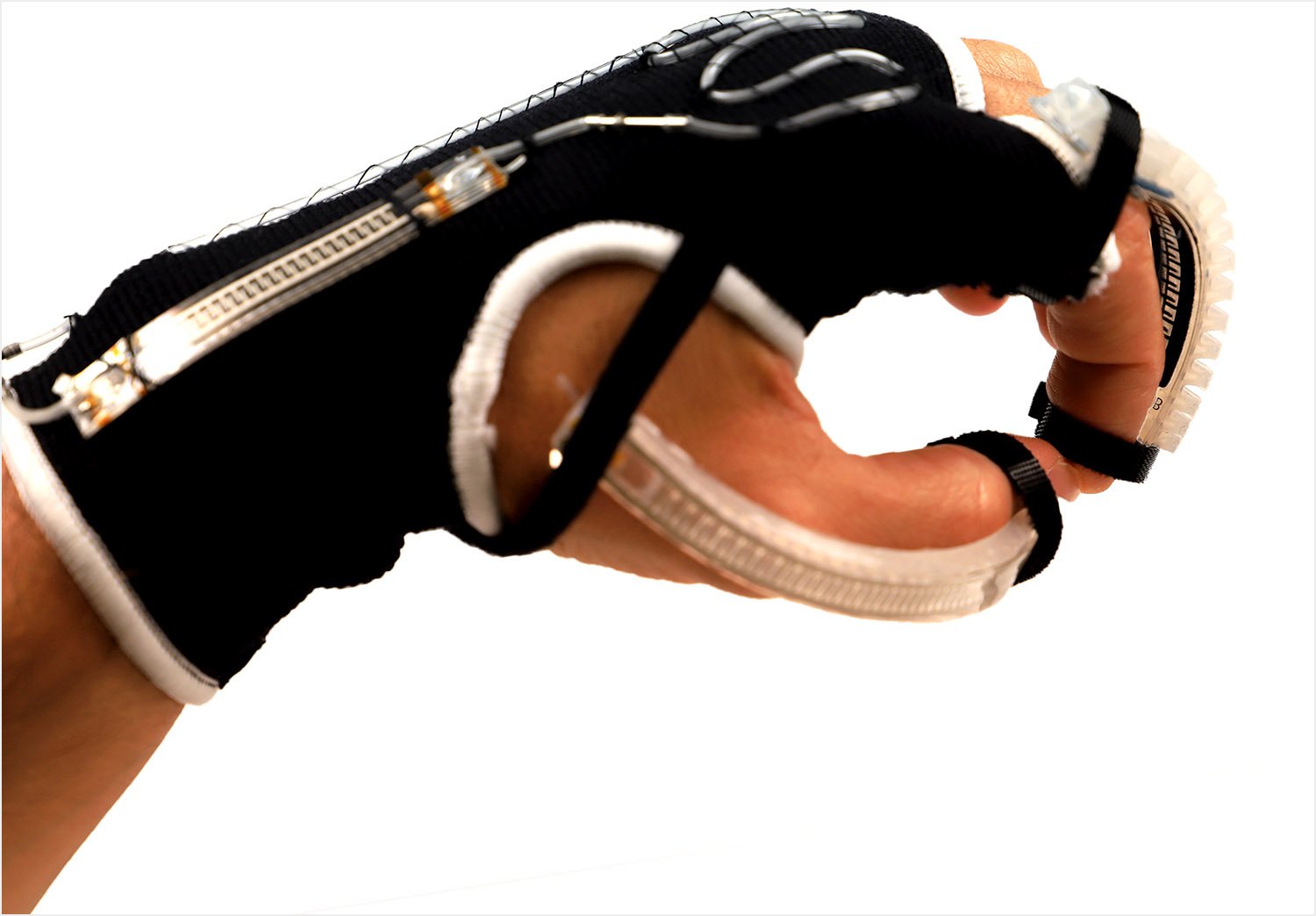
Wired for sound: A third wave emerges in integrated circuits
Optical fibres are our global nervous system, transporting terabytes of data across the planet in the blink of an eye. As that information travels at the speed of light across the globe, the energy of the light waves bouncing around inside the silica and polymer fibres create tiny vibrations that lead to feedback packets of … Read more