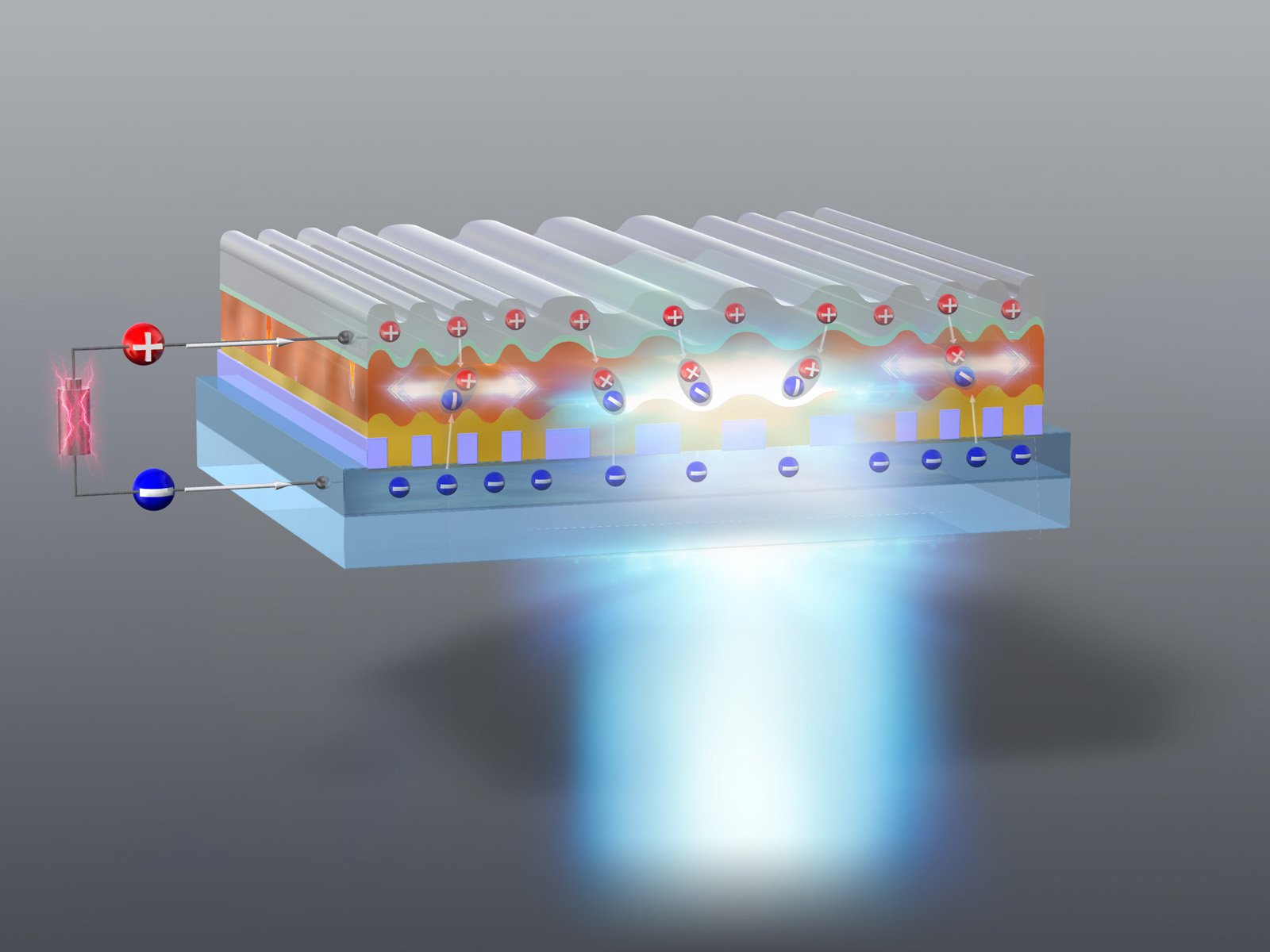
Targeting individual atoms
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy – NMR spectroscopy for short – is one of the most important methods of physicochemical analysis. It can be used to precisely determine molecular structures and dynamics. The importance of this method is also evidenced by the recognition of ETH Zurich’s two latest Nobel laureates, Richard Ernst and Kurt Wüthrich, for … Read more