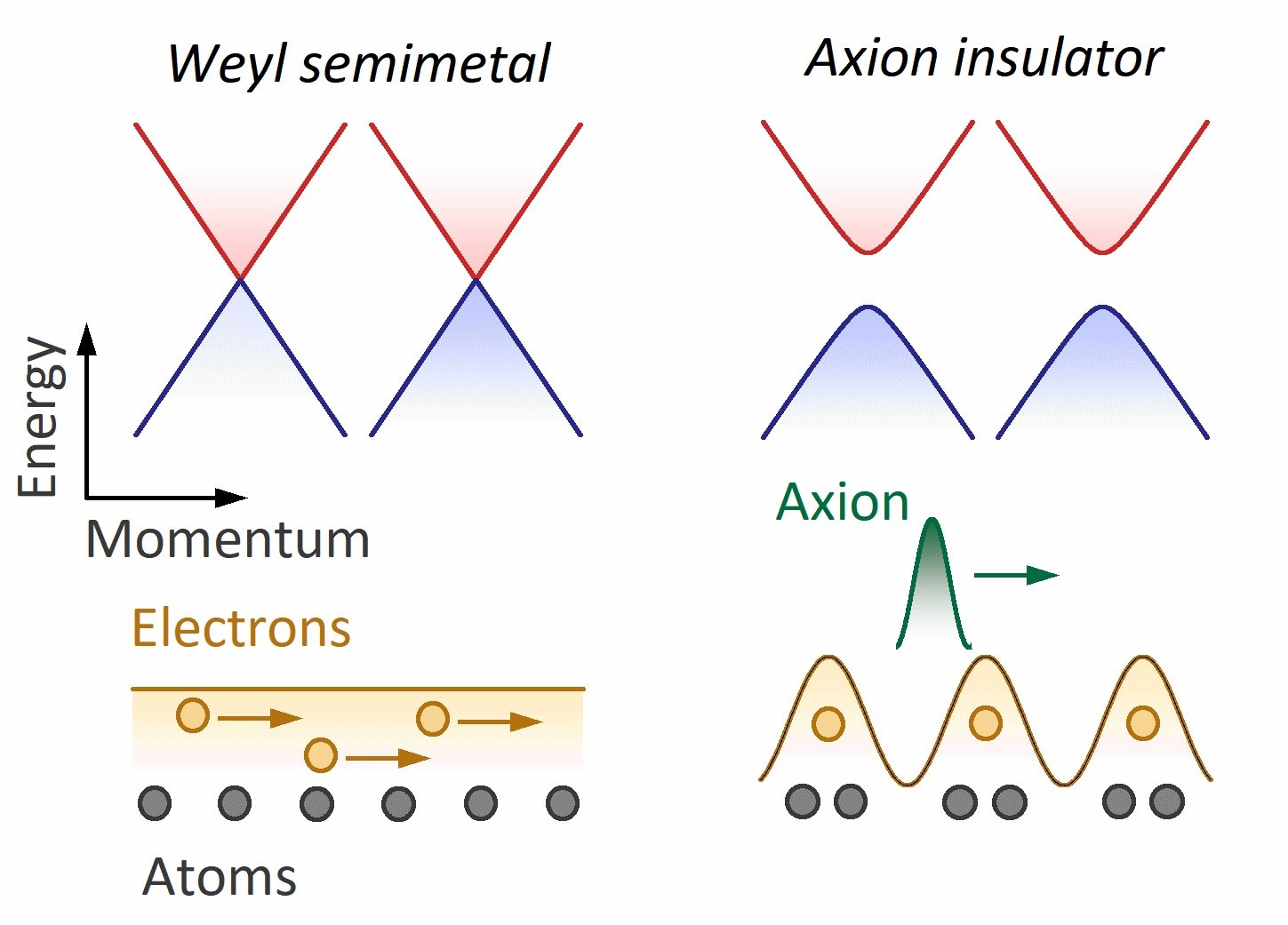
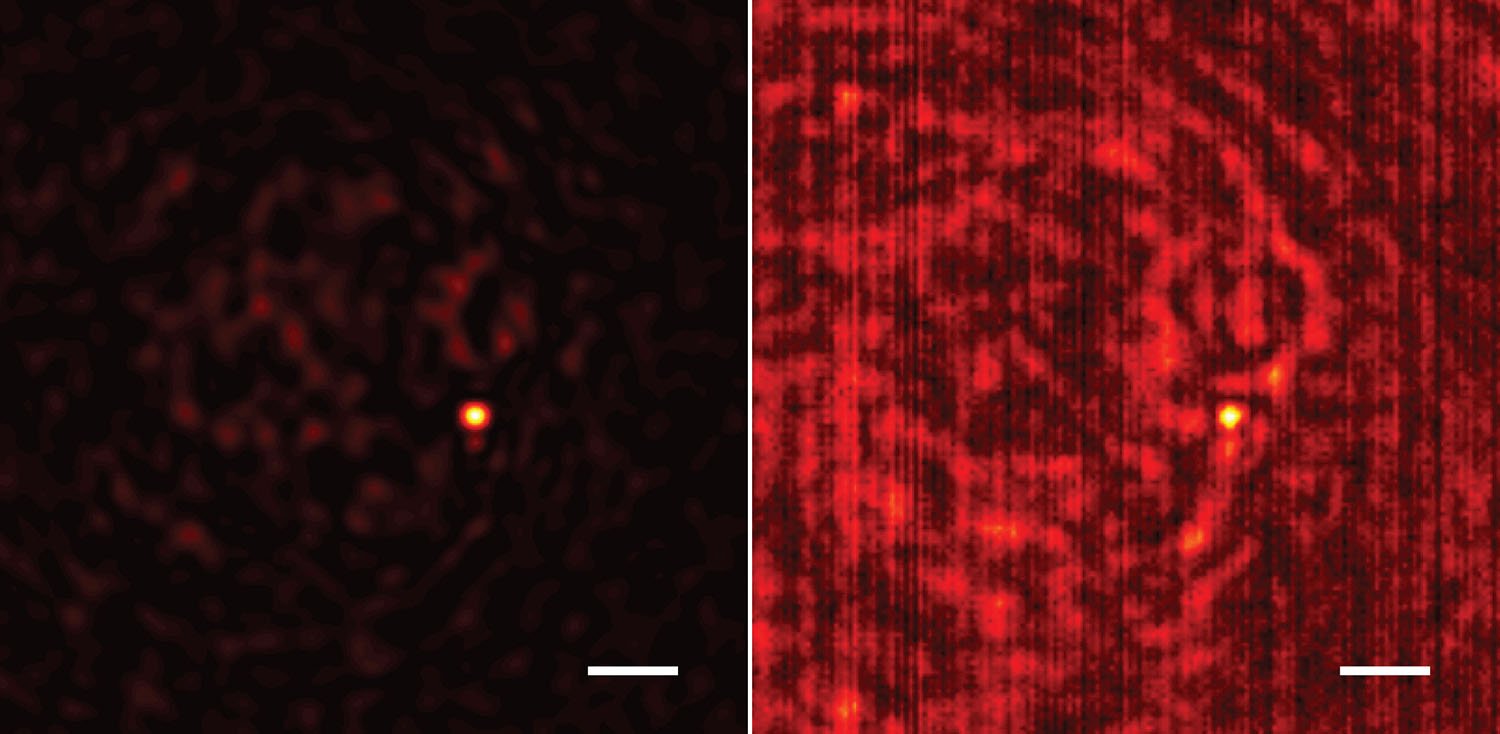
Axion particle spotted in solid-state crystal
Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Chemical Physics of Solids in Dresden, Princeton University, the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and the University of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have spotted a famously elusive particle: The axion – first predicted 42 years ago as an elementary particle in extensions of the standard model of … Read more