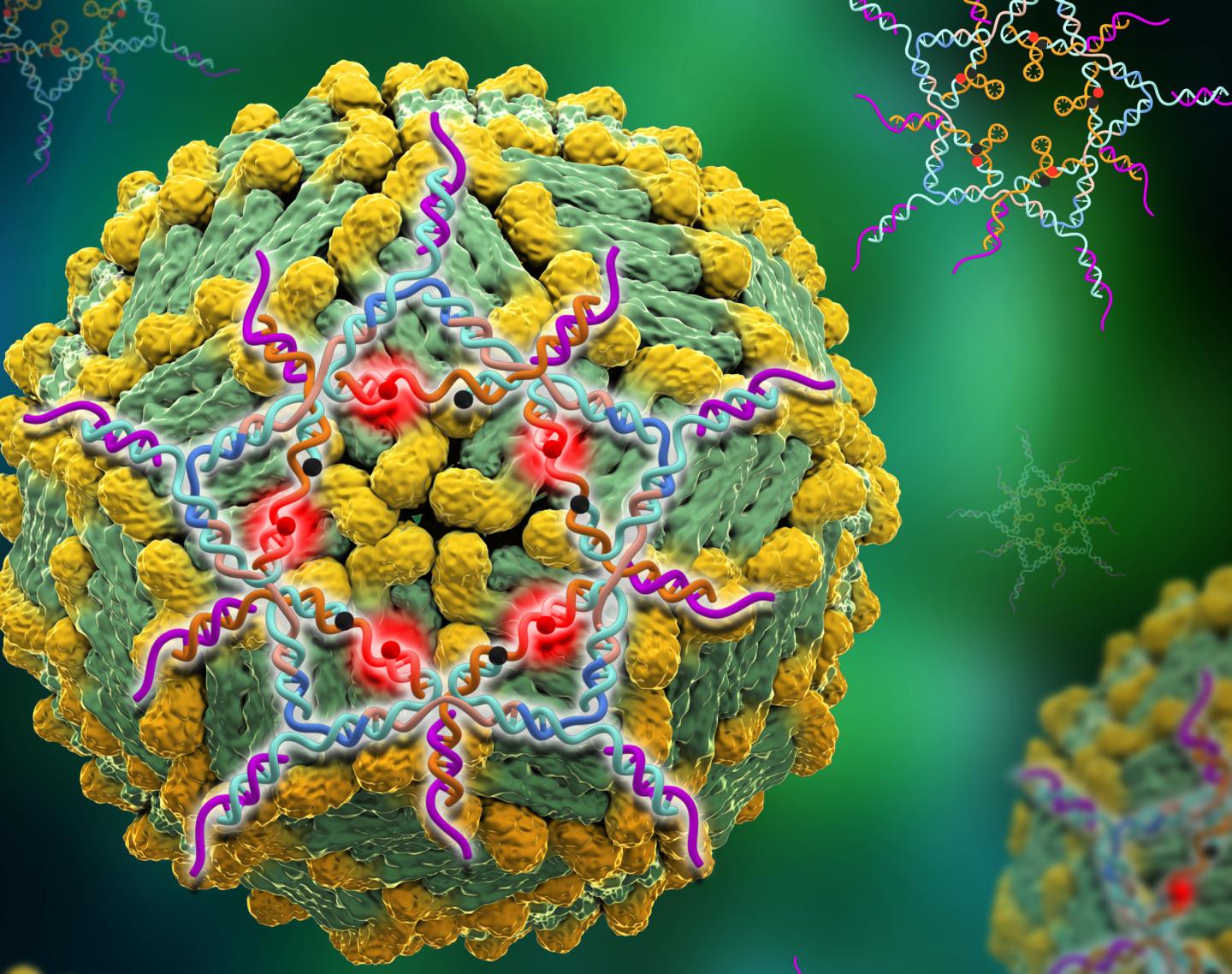
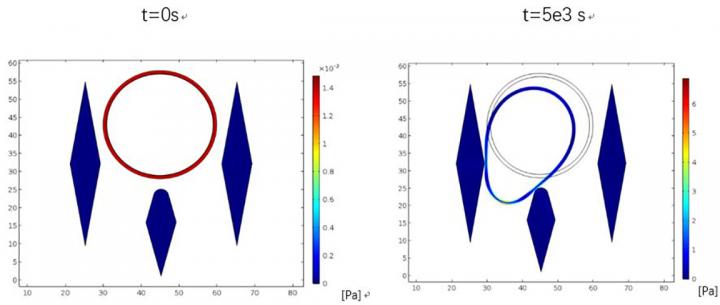
Structurally designed DNA star creates ultra-sensitive test for dengue virus
By folding snippets of DNA into the shape of a five-pointed star using structural DNA nanotechnology, researchers have created a trap that captures Dengue virus as it floats in the bloodstream. Once sprung, the trap – which is non-toxic and is naturally cleared from the body – lights up. It’s the most sensitive test for … Read more