Hope for coral recovery may depend on good parenting
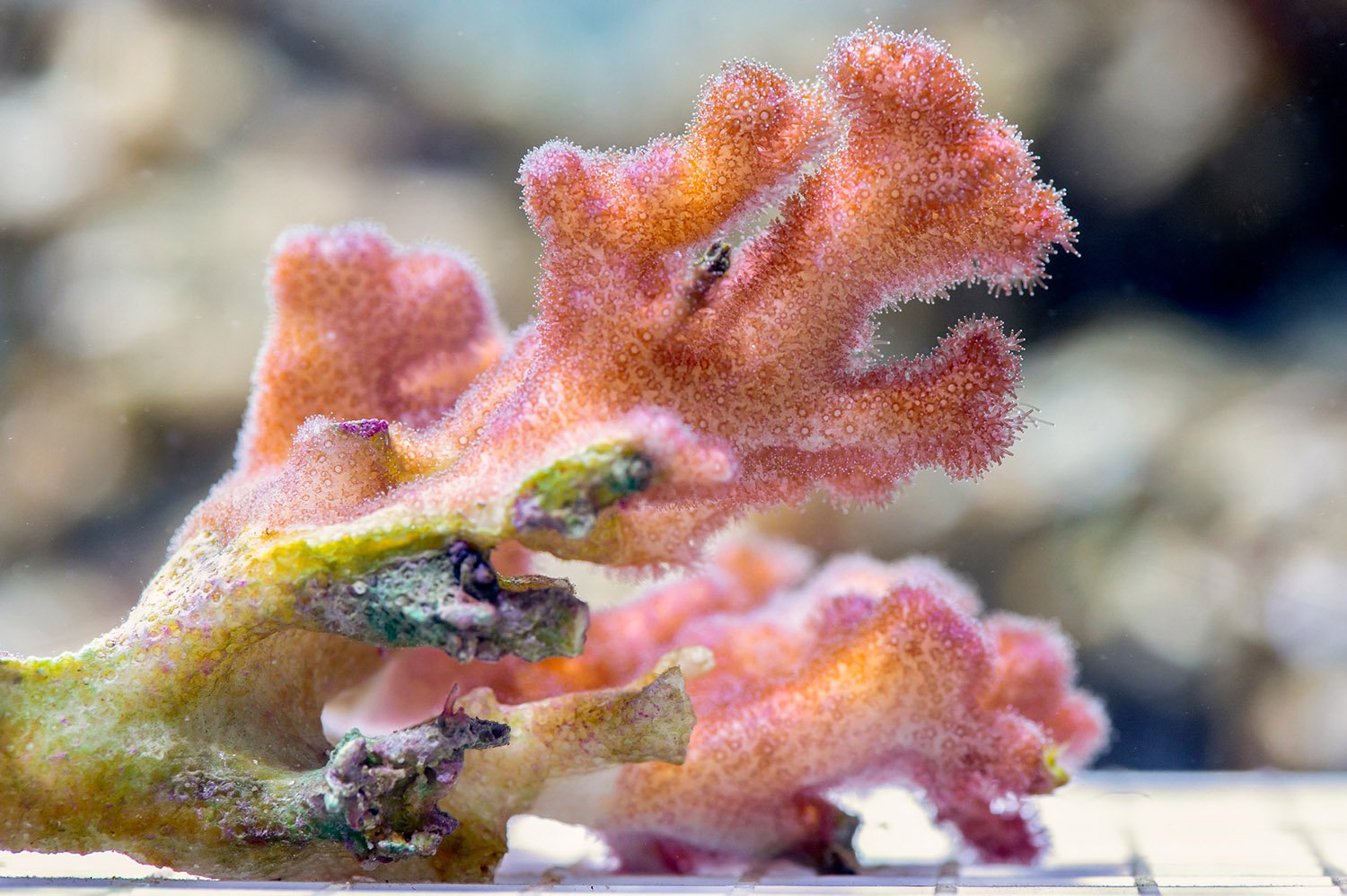
The fate of the world’s coral reefs could depend on how well the sea creatures equip their offspring to cope with global warming. About half the world’s coral has been lost due to warming seas that make their world hostile. Instead of vivid and floral, coral bleach pale as temperatures rise. This happens because the … Read more