Switching on the Atlantic heat pump
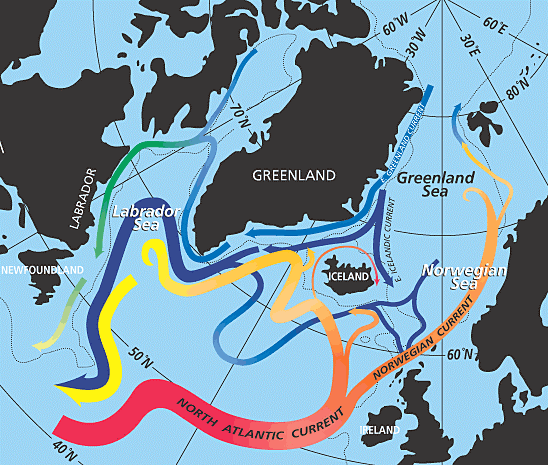
“We have found a new trigger to explain the start-up of the Atlantic current system during the greenhouse-icehouse climate transition: During the warm climate, buoyant fresh water flooded out of the Arctic and prevented the ocean-sinking that helps power the conveyor. We found that the Arctic-Atlantic gateway closed due to tectonic forces, causing a dramatic … Read more