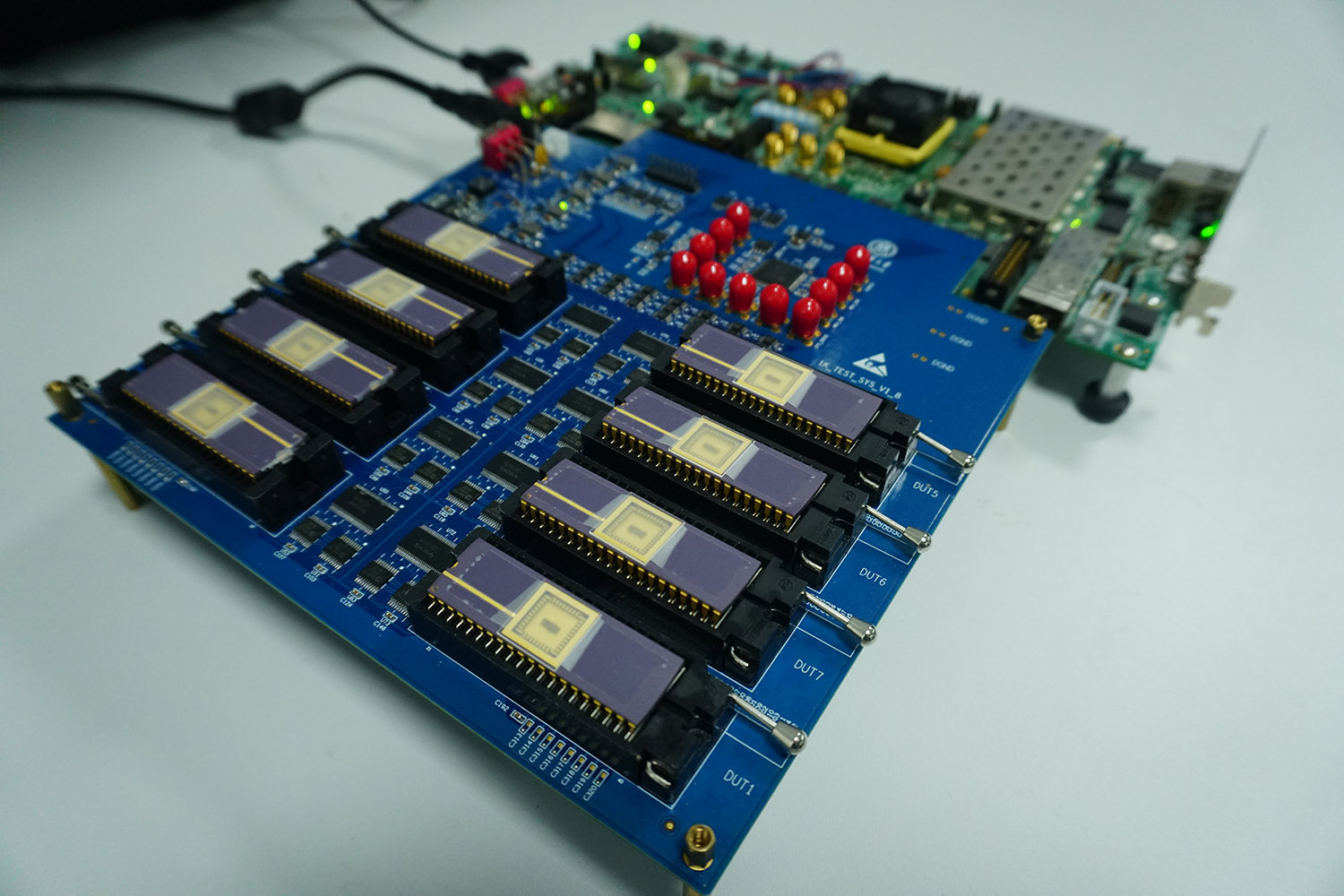
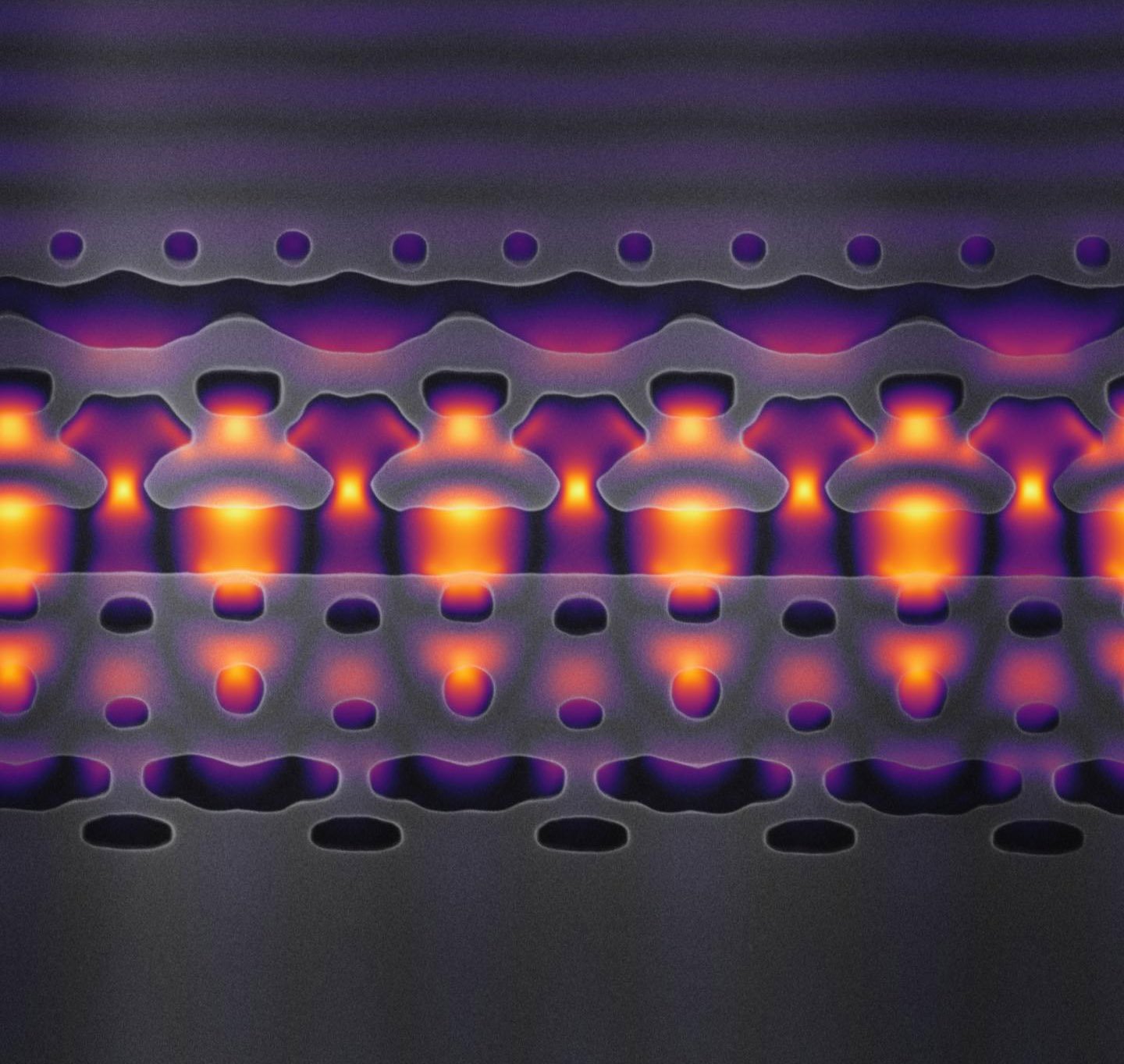
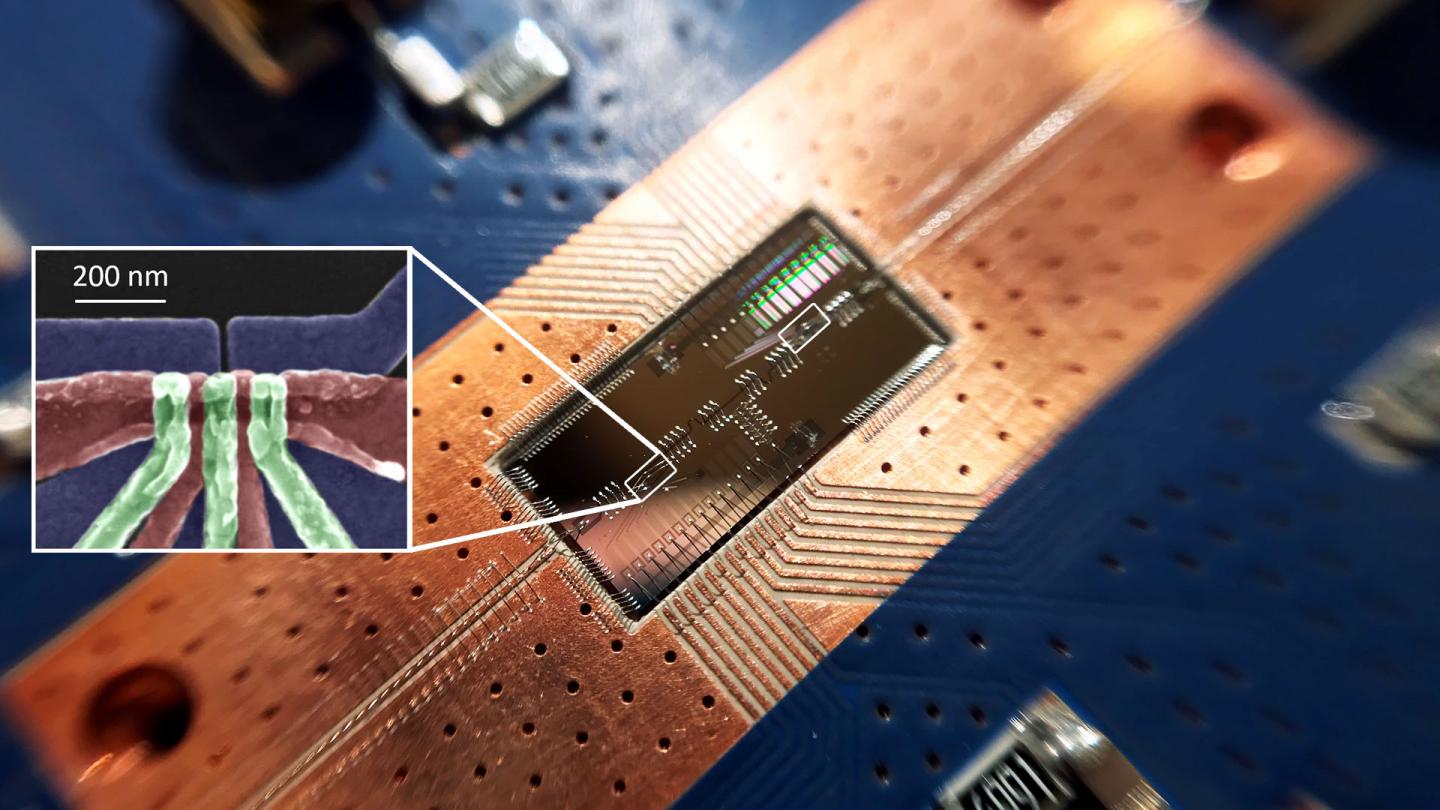
Novel memristor-enabled computation in memory architecture could revolutionize artificial-intelligence hardware
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revived these years because of the development of deep learning algorithms, which perform excellently in computer vision tasks (e.g. image recognition, detection) and nature language processing (e.g. machine translation, text generation). This is promising to revolutionize our society to enter an intelligent era. However, the fundamental computing hardware still face severe … Read more