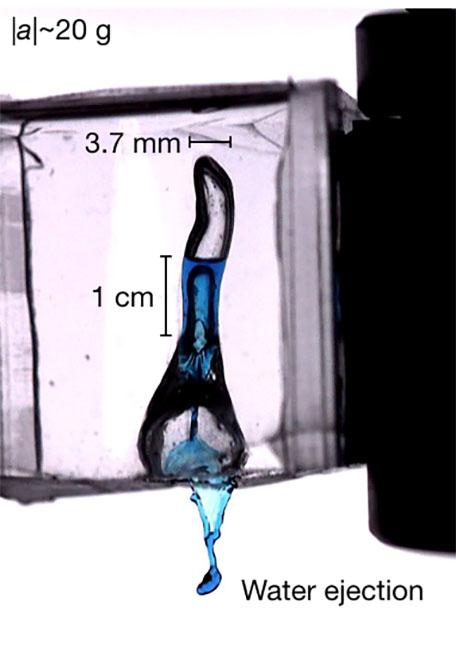
Shaking head to get rid of water in ears could cause brain damage
Trapped water in the ear canal can cause infection and even damage, but it turns out that one of the most common methods people use to get rid of water in their ears can also cause complications. Researchers at Cornell University and Virginia Tech show shaking the head to free trapped water can cause brain … Read more