Global warming and extinction risk
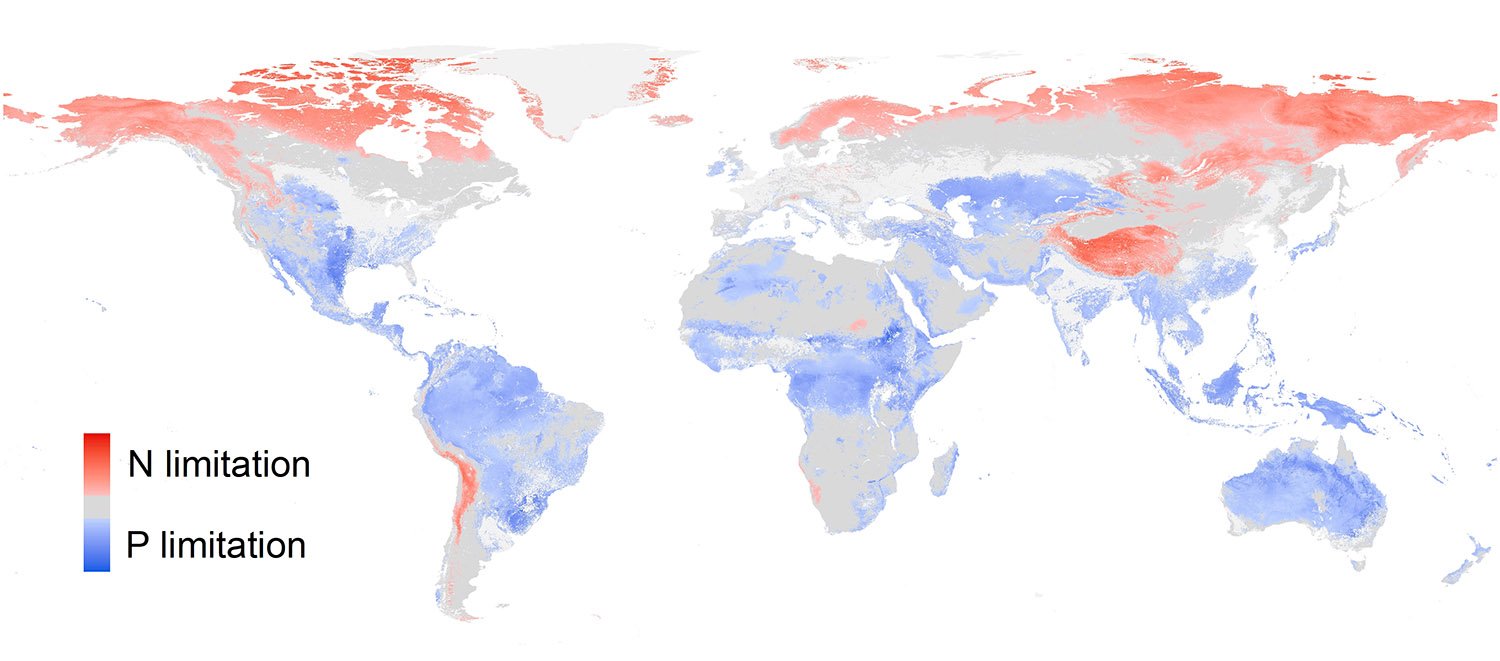
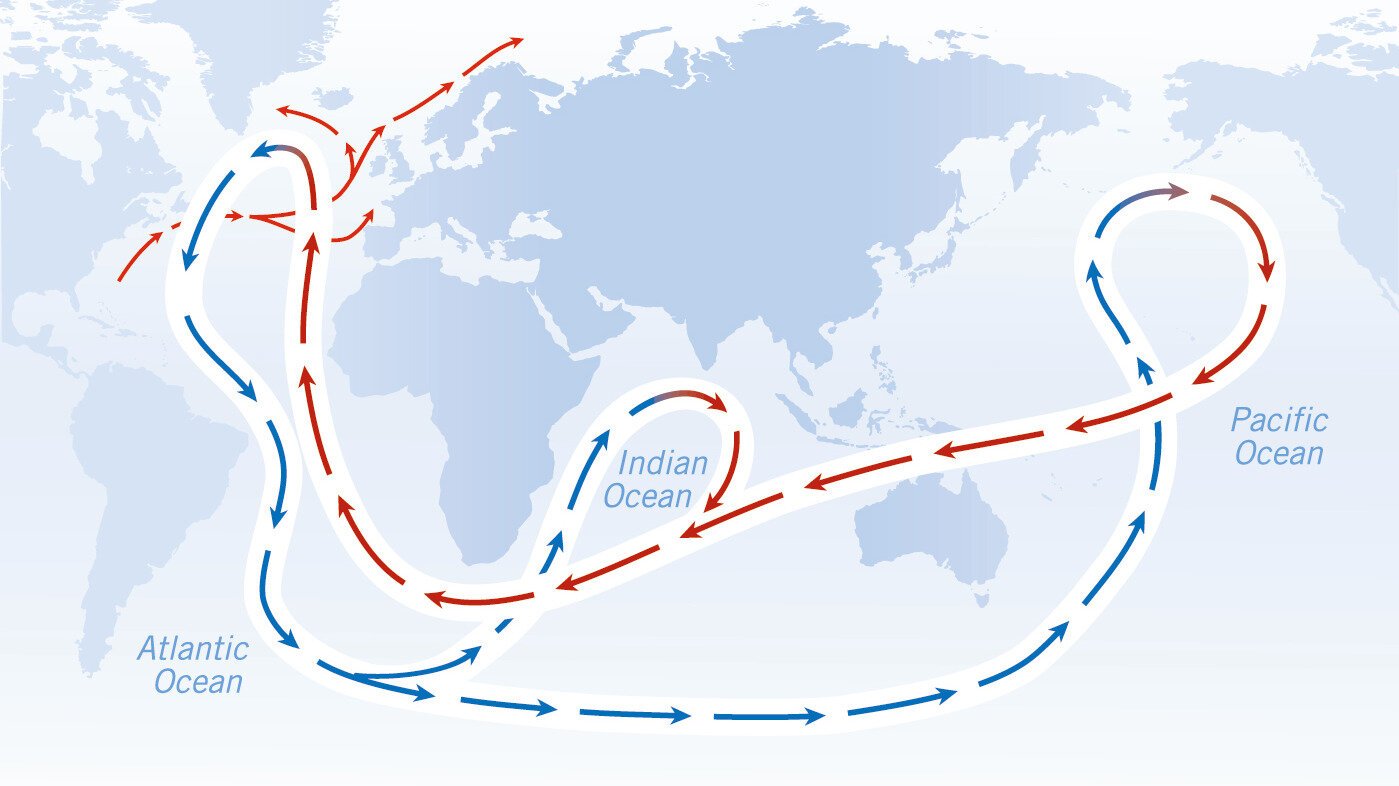
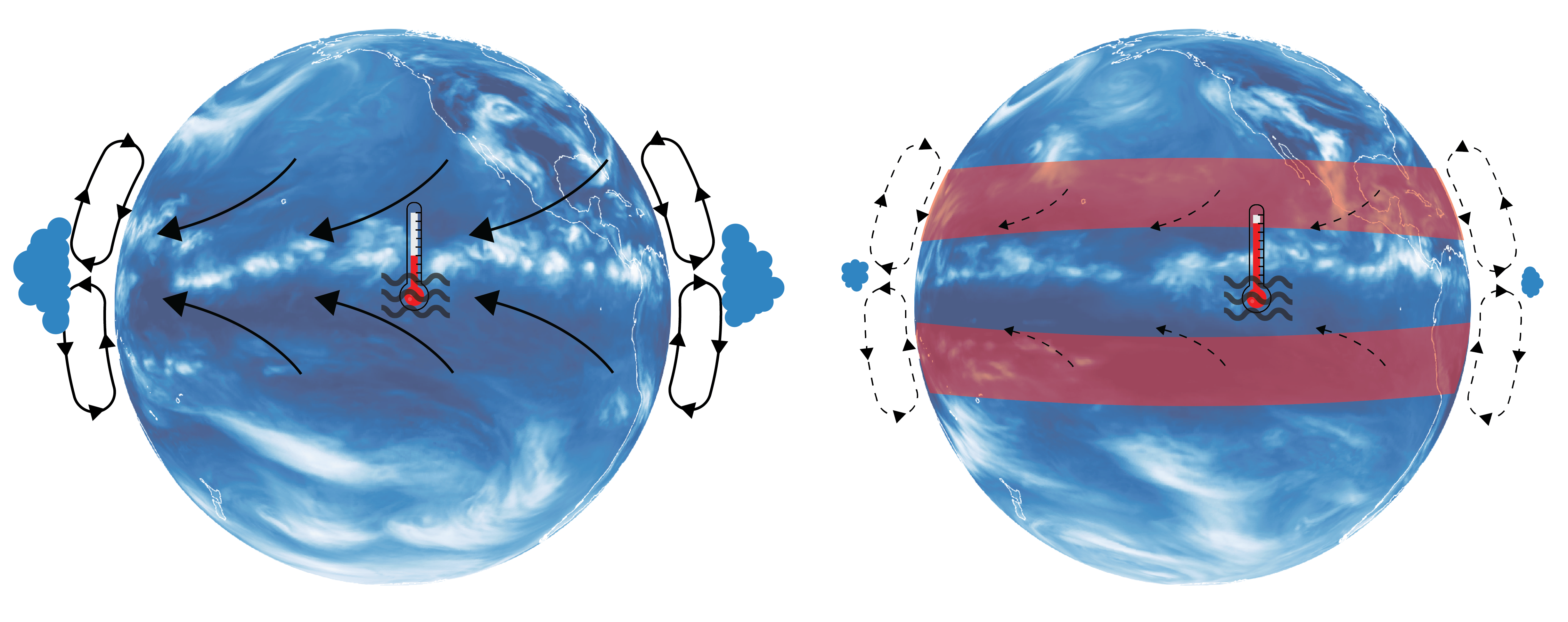
How can fossils predict the consequences of climate change? A German research team from Friedrich-Alexander Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg (FAU), the Museum of Natural History Berlin and the Alfred Wegener Institute compared data from fossil and marine organisms living today to predict which groups of animals are most at risk from climate change. They published their results … Read more