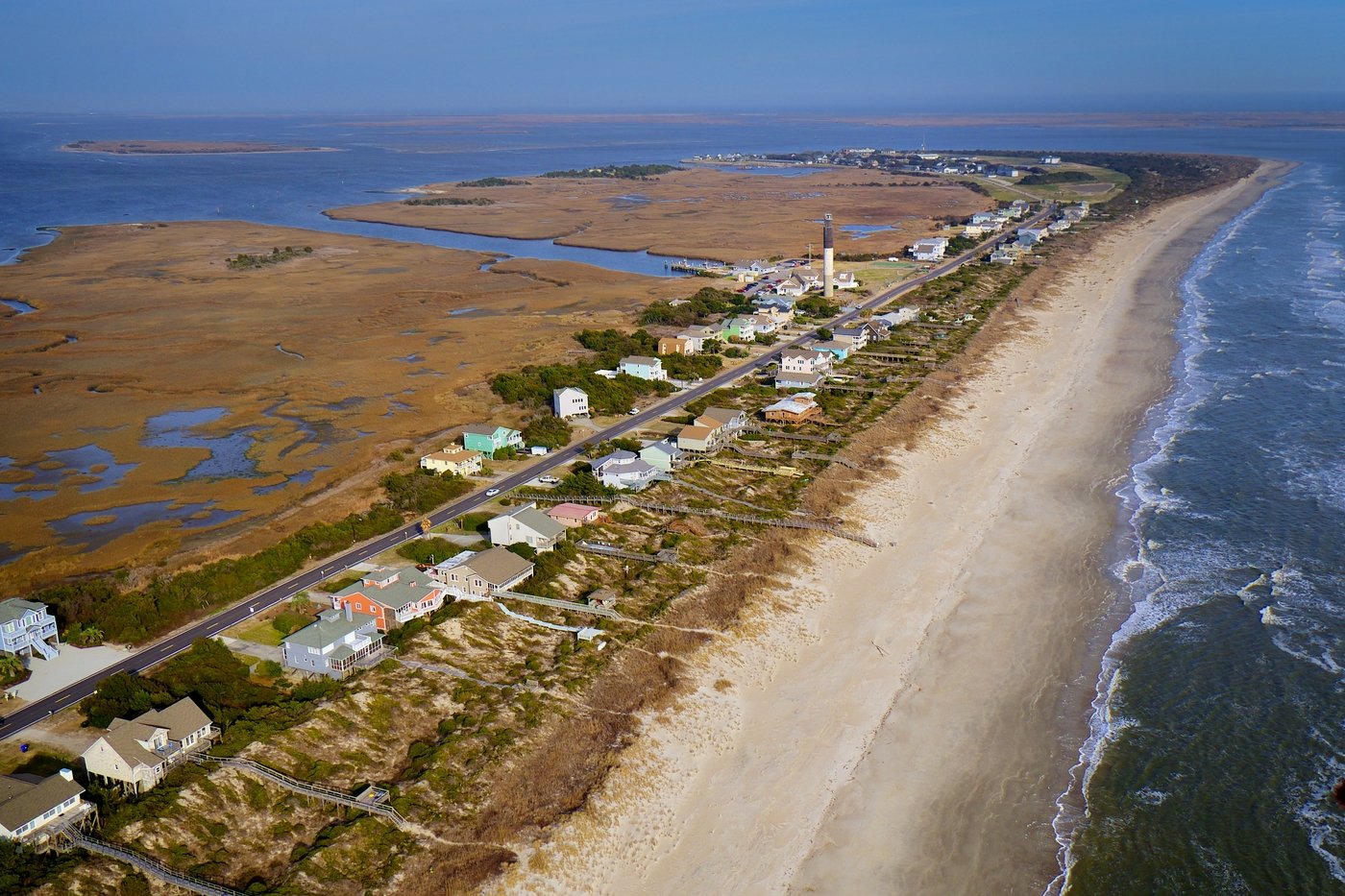
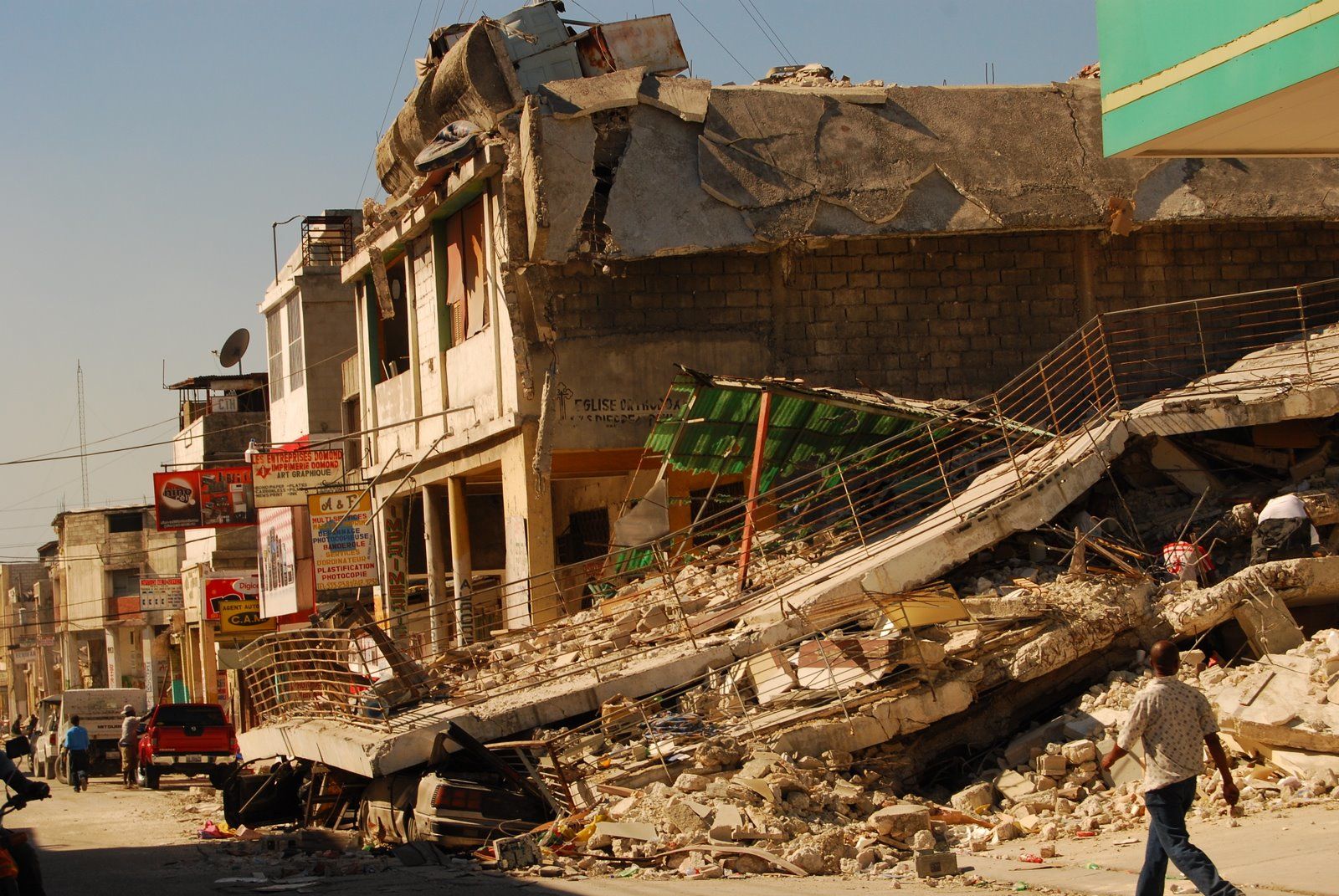
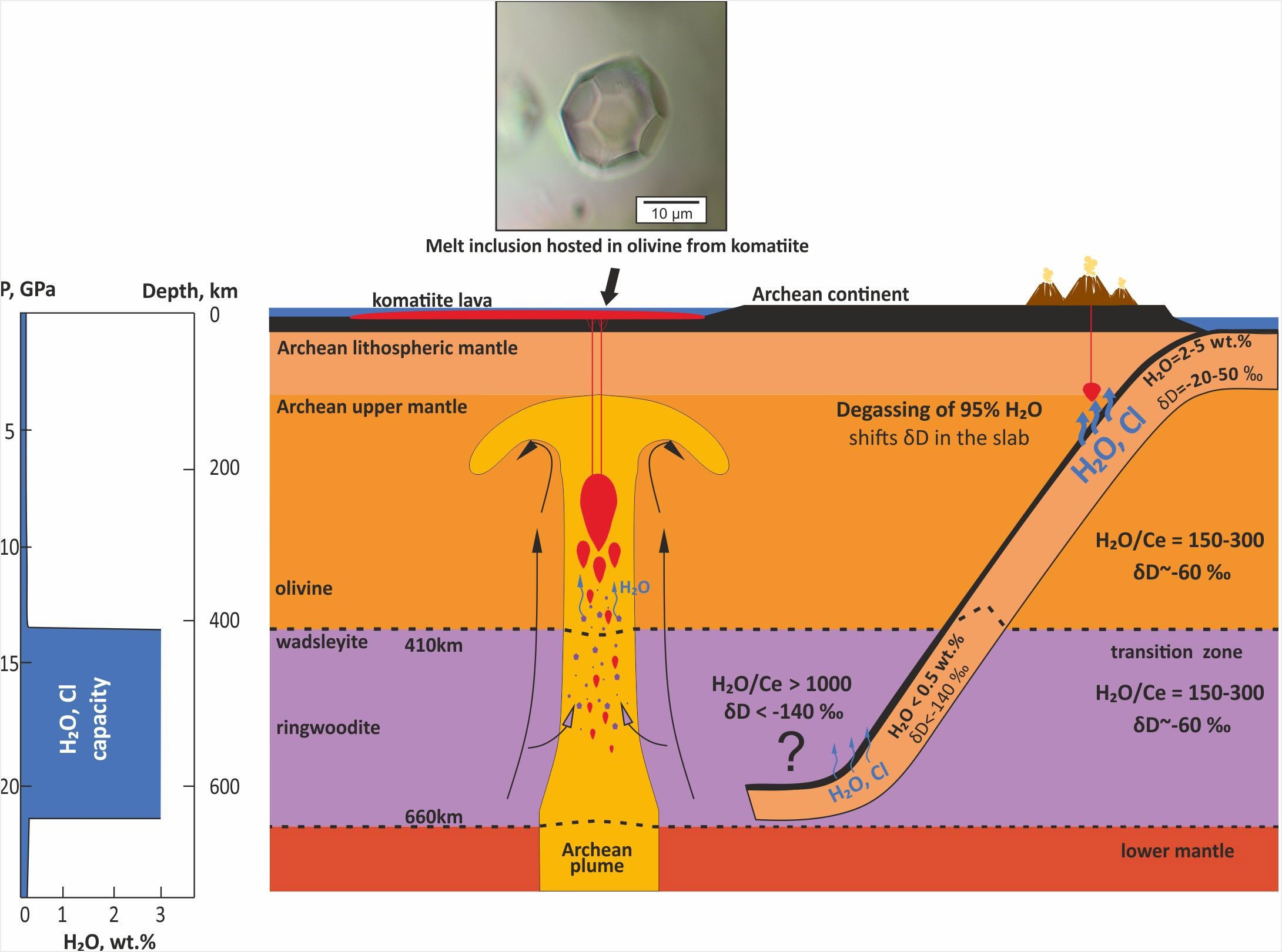
North Carolina coastal flooding is worsening with climate change, population growth
A historic 120-year-old data set is allowing researchers to confirm what data modeling systems have been predicting about climate change: Climate change is increasing precipitation events like hurricanes, tropical storms and floods. Researchers analyzed a continuous record kept since 1898 of tropical cyclone landfalls and rainfall associated with Coastal North Carolina storms. They found that … Read more