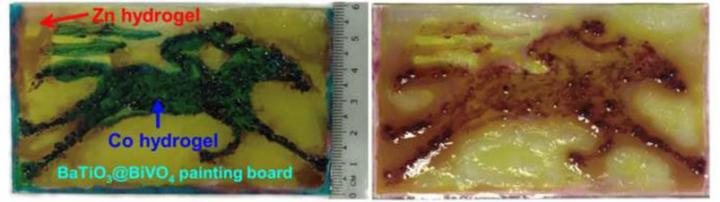
This humidity digester breathes in atmospheric water and exhales energy
Integrating a super moisture-absorbent gel with light-active materials, researchers in Singapore have developed a humidity digester to dry the ambient air while generating energy. The method, presented November 20 in the journal Joule, is a green alternative to air conditioners with a trick – pulling water out of thin air. Like plants, artificial photosynthetic devices, also … Read more